Enlargement of Thyroid: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
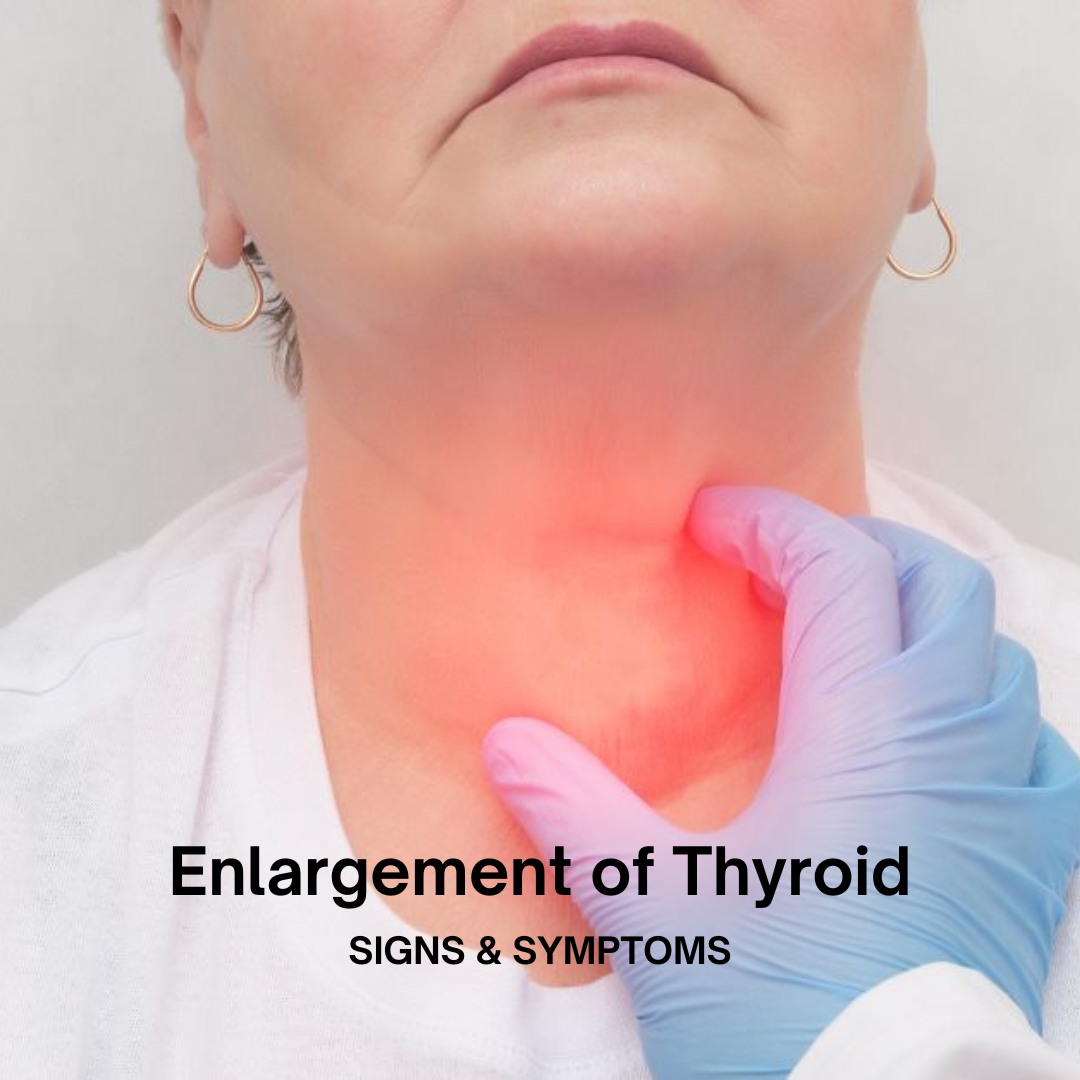
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of your neck, plays a crucial role in regulating your body’s metabolism. When the thyroid becomes enlarged, a condition known as a goiter, it can lead to various health issues. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for thyroid enlargement, providing you with comprehensive insights to better understand and manage this condition.
What is Thyroid Enlargement?
Thyroid enlargement, or goiter, refers to the abnormal growth of the thyroid gland. This condition can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender, though it is more common in women and older adults. Goiters can vary in size and may be associated with normal, decreased, or increased thyroid hormone levels.
Causes of Thyroid Enlargement
Several factors can lead to the enlargement of the thyroid gland, including:
- Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. A lack of iodine in the diet is a common cause of goiter worldwide.
- Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, causing it to produce excess hormones and enlarge.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Another autoimmune condition, Hashimoto’s disease leads to inflammation and damage of the thyroid, often resulting in an underactive thyroid and enlargement.
- Thyroid Nodules: Lumps or nodules can develop in the thyroid, causing it to enlarge. These nodules can be benign or, in rare cases, cancerous.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid gland can cause it to swell, leading to a temporary or permanent enlargement.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can sometimes cause the thyroid gland to enlarge.
Symptoms of Thyroid Enlargement
The symptoms of thyroid enlargement can vary depending on the underlying cause and the size of the goiter. Common symptoms include:
- Visible swelling at the base of the neck
- Tightness or discomfort in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Hoarseness or changes in voice
- Coughing
In some cases, goiters may not cause any noticeable symptoms and are only discovered during a routine medical examination.
Diagnosis of Thyroid Enlargement
To diagnose thyroid enlargement, healthcare providers typically perform a physical examination and may order additional tests, including:
- Blood Tests: To check levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
- Ultrasound: To visualize the thyroid gland and assess the presence of nodules or other abnormalities.
- Thyroid Scan: Using radioactive iodine to evaluate thyroid function and structure.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy: To collect a sample of thyroid tissue for further analysis, especially if nodules are present.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Enlargement
The treatment for thyroid enlargement depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. Common treatment options include:
- Observation: Small goiters that are not causing symptoms or affecting thyroid function may only require regular monitoring.
- Medications:
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement: Used to treat hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and shrink the goiter.
- Antithyroid Medications: Used to treat hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and reduce thyroid hormone production.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: Used to shrink the thyroid gland in cases of hyperthyroidism or large goiters.
- Surgery: In cases where the goiter is large, causing significant symptoms, or suspected to be cancerous, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland may be necessary.
Preventing Thyroid Enlargement
While not all cases of thyroid enlargement can be prevented, some measures can reduce the risk:
- Ensure adequate iodine intake through diet or supplements, especially in areas where iodine deficiency is common.
- Regular medical check-ups to monitor thyroid health and function.
- Awareness of family history, as some thyroid conditions may have a genetic component.
Conclusion
Thyroid enlargement is a common condition with various causes and symptoms. Understanding the underlying reasons and available treatment options can help manage and alleviate the effects of a goiter. If you suspect you have an enlarged thyroid or are experiencing related symptoms, consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.