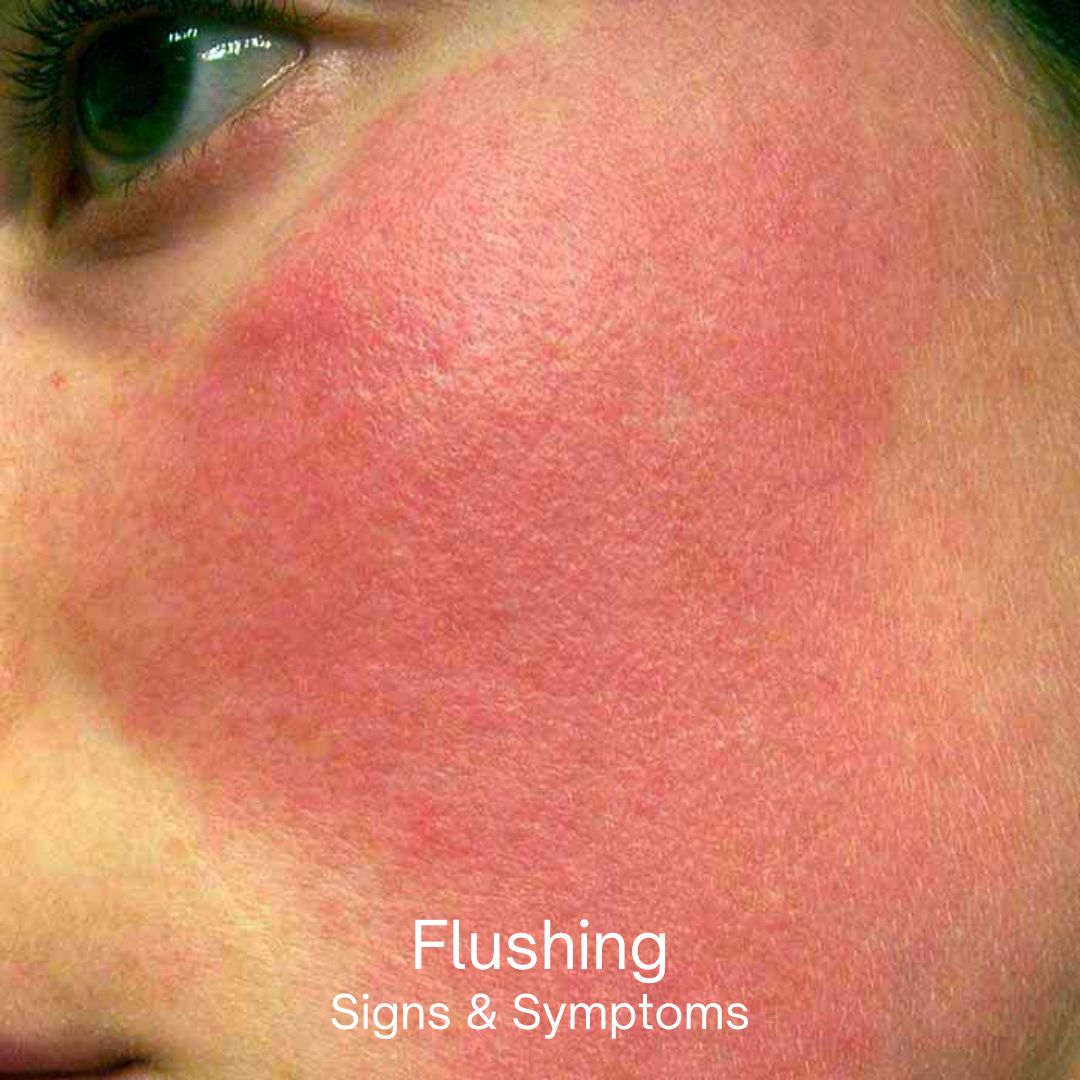
Flushing: A Comprehensive Overview
Flushing, a common physiological phenomenon, manifests as a sudden reddening of the skin, typically occurring in the face and neck. This condition results from the dilation of blood vessels, which increases blood flow to the skin’s surface. While flushing is generally harmless and temporary, it can sometimes indicate underlying health issues. This article explores the various causes, symptoms, and treatments associated with flushing, providing a thorough understanding of this intriguing bodily response.
Causes of Flushing
Flushing can be triggered by a wide range of factors, from emotional responses to medical conditions. Here are some of the most common causes:
-
Emotional Triggers:
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress and anxiety are significant triggers for flushing. When a person is anxious or stressed, the body’s fight-or-flight response is activated, leading to the release of adrenaline. This hormone causes blood vessels to dilate, resulting in a flushed appearance.
- Embarrassment: Blushing is a form of flushing specifically related to emotional responses like embarrassment or shame. It is a natural reaction caused by the activation of the sympathetic nervous system.
-
Dietary Triggers:
- Spicy Foods: Consuming spicy foods can cause a temporary increase in blood flow to the skin, leading to flushing. Capsaicin, the active ingredient in chili peppers, stimulates nerve endings and increases blood flow.
- Alcohol: Drinking alcohol can cause the blood vessels to expand, leading to flushing. This reaction is more pronounced in some individuals, particularly those with alcohol intolerance.
-
Medical Conditions:
- Rosacea: Rosacea is a chronic skin condition characterized by persistent facial redness and flushing. It is often accompanied by small, red, pus-filled bumps.
- Menopause: Many women experience hot flashes and flushing during menopause due to hormonal changes, particularly the decrease in estrogen levels.
- Carcinoid Syndrome: This rare condition involves the release of certain chemicals by carcinoid tumors, leading to episodic flushing, diarrhea, and wheezing.
-
Medications:
- Niacin: High doses of niacin, a type of vitamin B3, can cause flushing. This side effect is usually harmless but can be uncomfortable.
- Certain Blood Pressure Medications: Medications like calcium channel blockers and nitrates can cause dilation of blood vessels, leading to flushing.
Symptoms of Flushing
The primary symptom of flushing is a sudden reddening of the skin, which can be accompanied by a sensation of warmth or heat. Flushing typically affects the face and neck but can also spread to the chest and other areas. In some cases, additional symptoms may accompany flushing, depending on the underlying cause:
- Rosacea: Persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and acne-like bumps.
- Menopause: Hot flashes, night sweats, and mood changes.
- Carcinoid Syndrome: Diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and wheezing.
Diagnosis of Flushing
Diagnosing the cause of flushing involves a comprehensive medical evaluation. A healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination. They may also order specific tests to identify underlying conditions, such as:
- Blood Tests: To check for hormonal imbalances, infections, or other abnormalities.
- Skin Biopsy: In cases where a skin condition like rosacea is suspected.
- 24-Hour Urine Test: To detect elevated levels of certain chemicals associated with carcinoid syndrome.
Treatment Options for Flushing
The treatment of flushing depends on its underlying cause. Here are some common treatment approaches:
-
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Stress Management: Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress and reduce stress-induced flushing.
- Dietary Changes: Avoiding known dietary triggers, such as spicy foods and alcohol, can help prevent flushing episodes.
-
Medications:
- Topical Treatments: For conditions like rosacea, topical creams containing metronidazole, azelaic acid, or ivermectin can help reduce redness and inflammation.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): For menopausal women experiencing hot flashes, HRT can help manage symptoms. However, it is essential to discuss the risks and benefits with a healthcare provider.
- Anti-anxiety Medications: In cases where anxiety or stress is a significant trigger, medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may be prescribed.
-
Medical Procedures:
- Laser Therapy: For persistent flushing and visible blood vessels, laser therapy can be effective. This treatment targets and reduces the appearance of blood vessels, improving skin appearance.
- Surgical Intervention: In rare cases of severe carcinoid syndrome, surgery to remove the tumor may be necessary.
Prevention of Flushing
Preventing flushing involves identifying and avoiding triggers. Here are some tips to help manage and prevent flushing episodes:
- Identify Triggers: Keep a diary to track flushing episodes and identify potential triggers, such as specific foods, drinks, or stressful situations.
- Skincare Routine: Use gentle skincare products and avoid harsh treatments that can irritate the skin and cause flushing.
- Stay Cool: In hot weather, stay in cool environments and use fans or air conditioning to prevent overheating.
Conclusion
Flushing is a common and often harmless physiological response, but it can sometimes indicate underlying health conditions that require medical attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for flushing, individuals can better manage this condition and improve their overall quality of life. If you experience persistent or severe flushing, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment. With the right approach, flushing can be effectively managed, allowing you to maintain a healthy and comfortable life.