Understanding Dehydration: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Dehydration is a common condition that occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, disrupting the balance of minerals and salts in the body. Proper hydration is crucial for maintaining optimal health, yet many people are unaware of the signs, causes, and preventive measures for dehydration. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of dehydration, its symptoms, causes, and effective strategies for prevention.
What is Dehydration?
Dehydration occurs when the body lacks the necessary amount of water to carry out its normal functions. Water is essential for various bodily processes, including regulating temperature, lubricating joints, and aiding in digestion. When the body becomes dehydrated, it can lead to severe health issues if not addressed promptly.
Symptoms of Dehydration
Recognizing the symptoms of dehydration is crucial for early intervention. Common signs include:
- Thirst: One of the earliest indicators of dehydration.
- Dry Mouth and Skin: Lack of moisture in the mouth and dry, flaky skin.
- Dark Yellow Urine: Indicates concentrated urine due to low water intake.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired and lethargic.
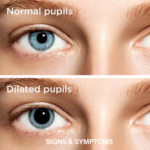
- Dizziness: Light-headedness or dizziness, especially when standing up quickly.
- Headache: Dehydration can often cause headaches and migraines.
- Confusion: Severe dehydration can lead to confusion and cognitive impairment.
Causes of Dehydration
Several factors can contribute to dehydration, including:
- Inadequate Water Intake: Not drinking enough water, especially in hot weather or during physical activity.
- Excessive Sweating: High levels of physical activity or hot climates can cause significant fluid loss through sweat.
- Illness: Conditions such as fever, vomiting, and diarrhea can rapidly deplete the body’s fluids.
- Certain Medications: Diuretics and other medications can increase urination and fluid loss.
- Chronic Conditions: Diseases like diabetes can lead to increased fluid loss and dehydration.
Prevention of Dehydration
Preventing dehydration is essential for maintaining good health. Here are some effective strategies:
- Drink Plenty of Water: Aim to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water a day. Increase intake during hot weather or physical activity.
- Eat Water-Rich Foods: Incorporate fruits and vegetables with high water content, such as cucumbers, watermelons, and oranges, into your diet.
- Monitor Fluid Loss: Pay attention to signs of fluid loss, such as sweating and urination, and compensate by drinking more water.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: These substances can increase fluid loss through urination.
- Use Electrolyte Solutions: For severe dehydration, especially after illness, use oral rehydration solutions to restore electrolyte balance.
Conclusion
Dehydration is a preventable condition that can have serious health implications if left untreated. By recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes, you can take proactive steps to ensure adequate hydration. Incorporate healthy hydration habits into your daily routine to maintain optimal health and wellbeing. Remember, staying hydrated is not just about drinking water but also about maintaining a balanced intake of fluids and electrolytes. Prioritize your hydration to enjoy a healthier, more energetic life.
4o