Understanding Inflammation: A Comprehensive Guide
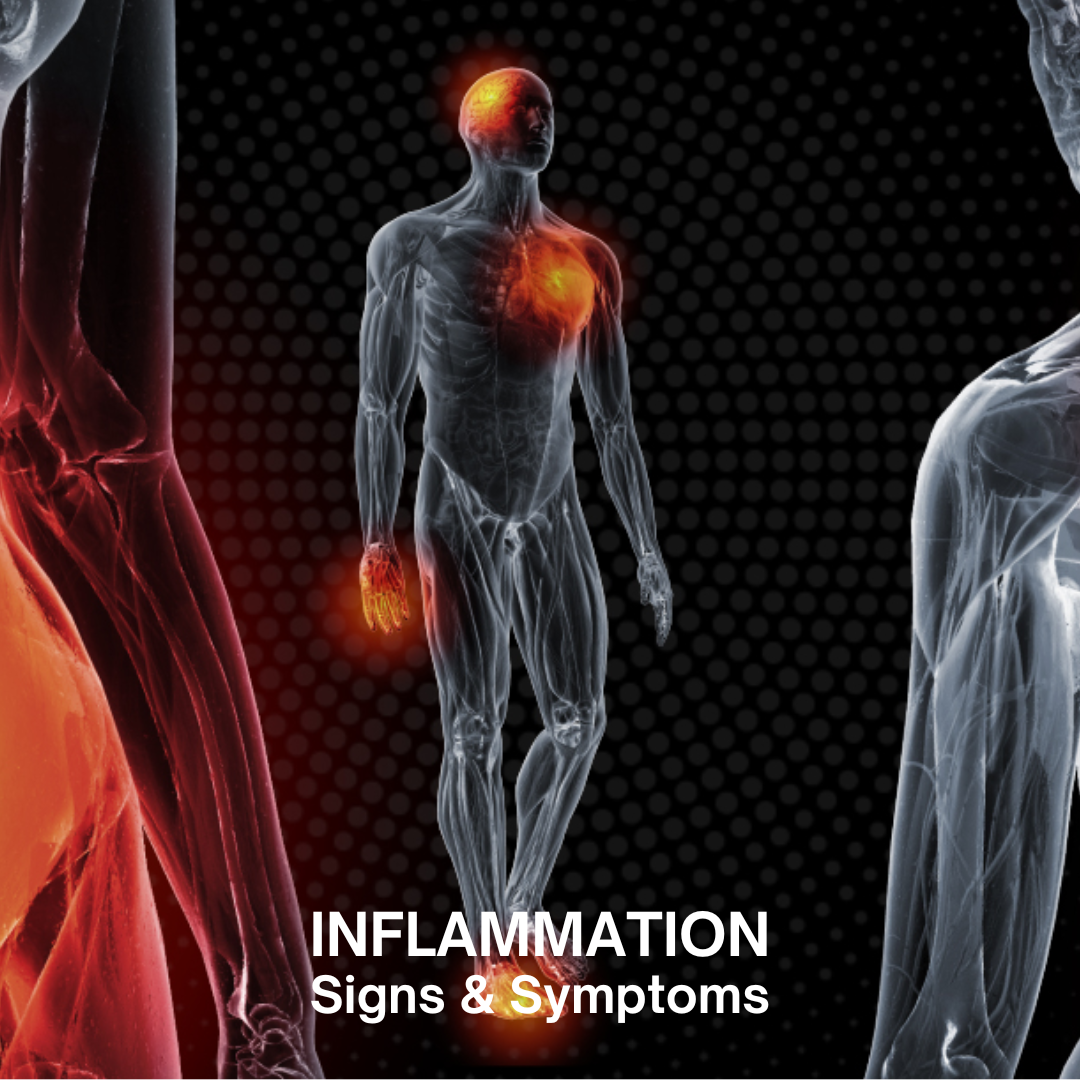
Inflammation is a crucial component of the body’s immune response. It is a natural process that occurs when the body attempts to heal itself after an injury, defend itself against foreign invaders like viruses and bacteria, and repair damaged tissue. However, while acute inflammation is beneficial, chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues. This article delves into the mechanisms, causes, types, effects, and management of inflammation.
The Mechanism of Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s way of signaling the immune system to heal and repair damaged tissues and defend itself against foreign invaders. When a harmful stimulus is detected, the immune system triggers an inflammatory response. This involves the release of inflammatory mediators such as histamine, prostaglandins, and cytokines, which increase blood flow to the affected area, leading to redness, heat, swelling, and pain.
The inflammatory response can be broken down into several stages:
- Initiation: When the body detects an injury or infection, immune cells like macrophages and mast cells release signaling molecules (cytokines) that trigger the inflammatory response.
- Amplification: More immune cells are recruited to the site of injury or infection. Blood vessels dilate to allow more blood flow, and the permeability of blood vessel walls increases to let immune cells and proteins move into the affected tissue.
- Destruction of Pathogens: Immune cells, including neutrophils and macrophages, engulf and destroy pathogens and debris.
- Resolution: Anti-inflammatory signals promote the repair of tissue, removal of dead cells, and restoration of normal function.
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammation
Acute inflammation is a short-term response that usually manifests quickly and resolves within a few days. Common causes include infections, physical injuries, and allergic reactions. Symptoms typically include redness, heat, swelling, pain, and loss of function at the affected site.
Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is a prolonged inflammatory response that can last for months or even years. It occurs when the body fails to eliminate the cause of an acute inflammation, when an autoimmune response is triggered, or due to persistent irritants. Chronic inflammation is often less noticeable than acute inflammation but can lead to severe health problems over time, such as heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
Causes of Inflammation
The causes of inflammation can be categorized into external and internal factors:
- External Factors:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can trigger an inflammatory response.
- Physical Injury: Cuts, bruises, burns, and other physical injuries initiate inflammation to begin the healing process.
- Chemicals: Exposure to harmful chemicals can cause tissue damage and inflammation.
- Allergens: Substances like pollen, dust, and certain foods can trigger allergic inflammation.
- Internal Factors:
- Autoimmune Reactions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus involve the immune system attacking the body’s own tissues, leading to chronic inflammation.
- Metabolic Imbalances: Obesity, high blood sugar, and high cholesterol can contribute to chronic inflammation.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals have genetic variations that make them more susceptible to inflammatory conditions.
Effects of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation can have widespread effects on the body and contribute to various diseases and conditions:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Chronic inflammation can lead to atherosclerosis, where arteries become clogged with fatty deposits, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Cancer: Inflammation can promote the growth and spread of cancer cells. Chronic inflammation has been linked to cancers of the liver, stomach, and colon.
- Diabetes: Inflammatory mediators can interfere with insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis involve chronic inflammation as the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Chronic inflammation in the brain is associated with diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Managing Inflammation
Managing inflammation involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and alternative therapies. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Diet: An anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce chronic inflammation. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., fatty fish, flaxseeds), antioxidants (e.g., fruits and vegetables), and fiber (e.g., whole grains, legumes) are beneficial. Avoiding processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats is also important.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate inflammation. Techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can help manage inflammation. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate medication.
- Alternative Therapies: Practices like acupuncture, massage, and herbal supplements (e.g., turmeric, ginger) may help reduce inflammation for some individuals.
Conclusion
Inflammation is a natural and essential part of the body’s defense mechanism. While acute inflammation is beneficial for healing, chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues. Understanding the causes and effects of inflammation and adopting strategies to manage it can help maintain overall health and prevent chronic diseases. By making informed lifestyle choices and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can effectively manage inflammation and promote long-term wellbeing.