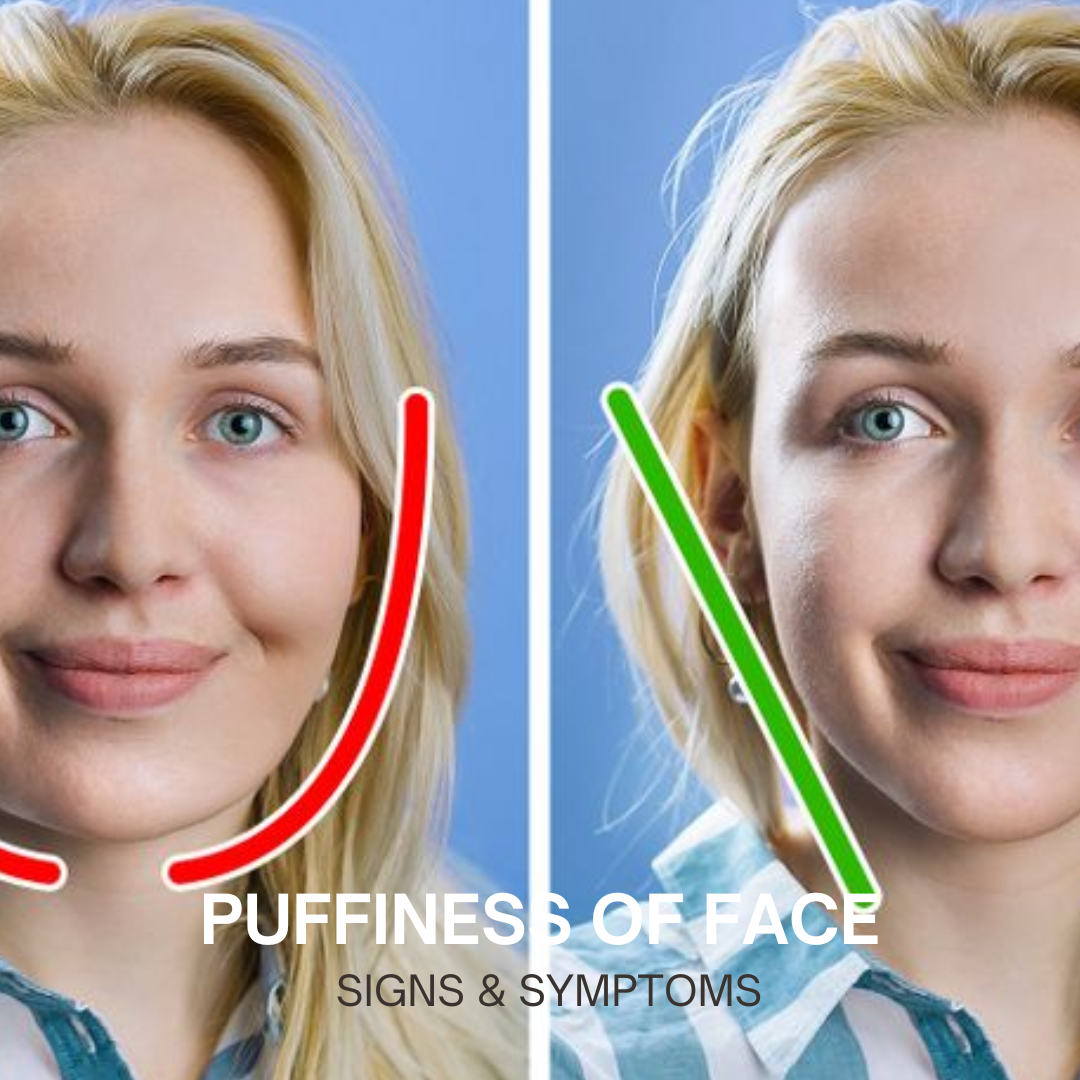
Puffiness of the Face: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
Puffiness of the face, often described as facial swelling or edema, is a common condition that can affect individuals of all ages. While it can be temporary and harmless, persistent or severe facial puffiness can be a sign of underlying health issues. This article explores the various causes, treatments, and preventive measures for facial puffiness.
Causes of Facial Puffiness
- Lifestyle Factors
- Diet: High salt intake can lead to water retention, causing facial puffiness. Processed foods and snacks are typical culprits.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can dehydrate the body, leading to fluid retention and facial swelling.
- Sleep Deprivation: Lack of sleep can cause fluid to accumulate around the eyes and face, resulting in puffiness.
- Stress: Chronic stress can affect the body’s fluid balance and contribute to facial swelling.
- Medical Conditions
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause inflammation and swelling in the face, especially around the eyes.
- Sinusitis: Sinus infections lead to congestion and swelling in the facial region.
- Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid can cause myxedema, which leads to facial puffiness.
- Kidney Problems: Kidney diseases can result in fluid retention, leading to swelling in the face and other parts of the body.
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can cause localized swelling and inflammation in the face.
- Hormonal Changes
- Menstruation: Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can lead to water retention and facial puffiness.
- Pregnancy: Increased fluid volume and hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause swelling in the face.
- Menopause: Hormonal changes during menopause can affect fluid balance and lead to puffiness.
- Environmental Factors
- Weather Changes: Extreme weather conditions, such as high humidity or cold temperatures, can cause facial swelling.
- Pollutants: Exposure to environmental pollutants can trigger allergic reactions and swelling.
Symptoms Accompanying Facial Puffiness
Facial puffiness can present with various symptoms, including:
- Swelling around the eyes (periorbital edema)
- Generalized facial swelling
- Redness and warmth in the affected area
- Tenderness or pain
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing (in severe cases)
Diagnosing Facial Puffiness
To diagnose the underlying cause of facial puffiness, healthcare professionals may perform:
- Physical Examination: To assess the extent and location of the swelling.
- Medical History Review: To identify any underlying conditions or triggers.
- Blood Tests: To check for thyroid function, kidney function, and other relevant markers.
- Allergy Tests: To identify potential allergens.
- Imaging Tests: Such as X-rays or CT scans, to check for sinusitis or other structural issues.
Treatment Options for Facial Puffiness
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Changes: Reducing salt and alcohol intake can help decrease water retention. Incorporating more fruits and vegetables can improve overall health and reduce puffiness.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out excess sodium and reduces swelling.
- Sleep Hygiene: Ensuring adequate sleep can prevent fluid accumulation around the face.
- Home Remedies
- Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress to the swollen area can reduce inflammation and puffiness.
- Elevating the Head: Sleeping with the head elevated can prevent fluid from pooling in the face.
- Gentle Massage: Massaging the face can stimulate lymphatic drainage and reduce swelling.
- Medical Treatments
- Allergy Medications: Antihistamines can help manage allergic reactions and reduce swelling.
- Decongestants: For sinus-related puffiness, decongestants can relieve congestion and swelling.
- Diuretics: In cases of severe water retention, diuretics may be prescribed to help the body expel excess fluid.
- Corticosteroids: For inflammatory conditions, corticosteroids can reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Surgical Interventions
- In rare cases where puffiness is due to structural issues or chronic sinusitis, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct the underlying problem.
Preventing Facial Puffiness
- Maintain a Healthy Diet
- Reduce sodium intake and avoid processed foods.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Stay Hydrated
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain proper hydration.
- Manage Allergies
- Identify and avoid known allergens.
- Use allergy medications as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Practice Good Sleep Hygiene
- Ensure you get enough sleep each night.
- Use pillows to keep your head elevated if prone to puffiness.
- Reduce Stress
- Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol
- Limit alcohol consumption to prevent dehydration and fluid retention.
When to See a Doctor
While occasional facial puffiness is generally harmless, persistent or severe swelling warrants medical attention. Seek professional help if you experience:
- Sudden or severe facial swelling
- Swelling accompanied by difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Persistent puffiness without an obvious cause
- Signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or fever
Conclusion
Facial puffiness can be a minor inconvenience or a sign of an underlying health issue. Understanding the causes and implementing appropriate treatments can help manage and prevent this condition. By making simple lifestyle changes, using home remedies, and seeking medical advice when necessary, you can reduce facial puffiness and maintain a healthier, more comfortable life.