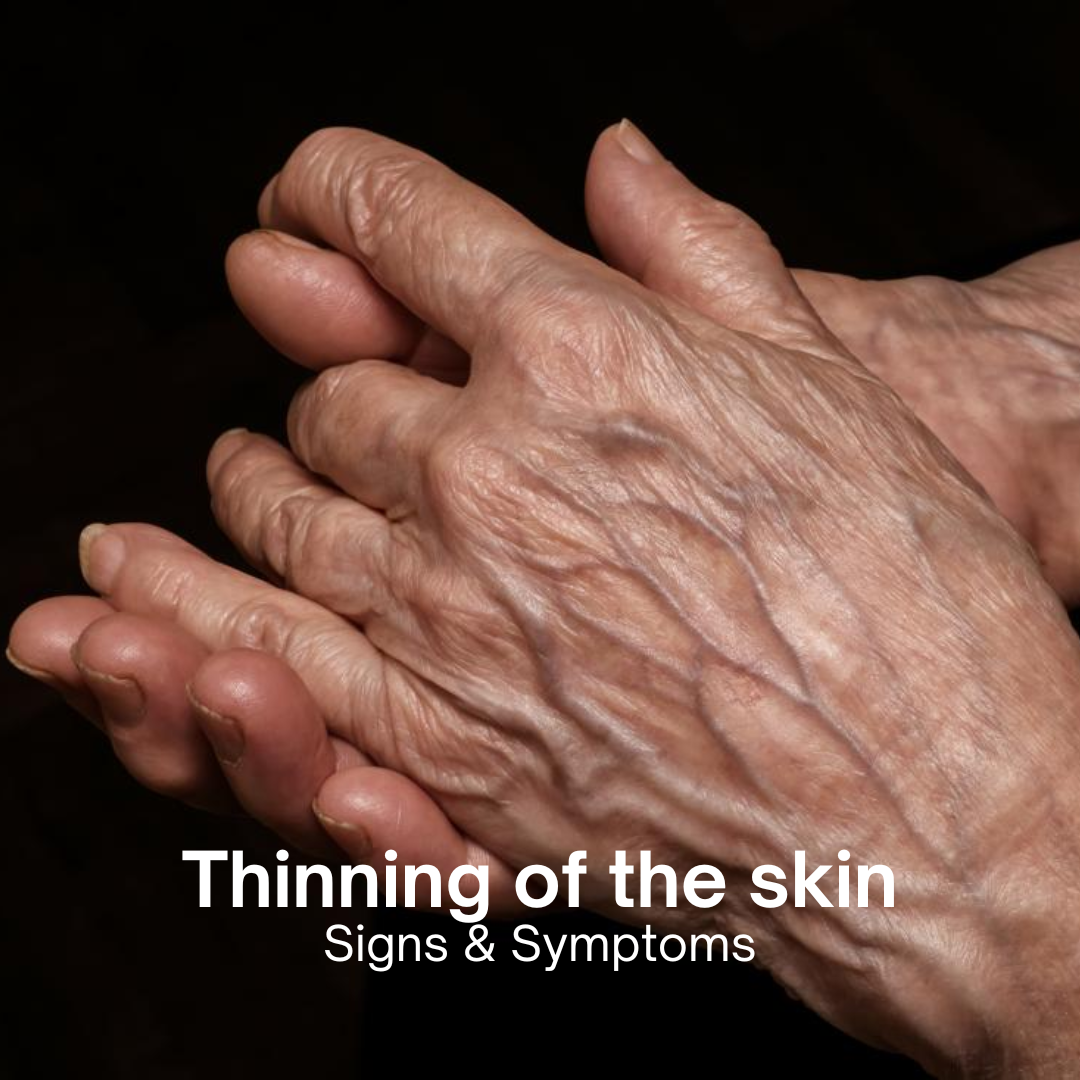
Thinning of the Skin: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Skin thinning, also known as skin atrophy, is a condition where the skin becomes fragile, less elastic, and more prone to bruising and tearing. This phenomenon can occur due to various factors, including aging, certain medical conditions, and prolonged use of specific medications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of thinning skin can help individuals manage this condition effectively.
Causes of Skin Thinning
- Aging:
- One of the primary causes of thinning skin is aging. As we grow older, our skin naturally loses some of its thickness and elasticity. The production of collagen and elastin, which are essential proteins for maintaining skin structure, decreases with age. Additionally, the fat layer beneath the skin becomes thinner, reducing its cushioning effect and making the skin more prone to damage.
- Genetics:
- Genetic factors play a significant role in determining the thickness of the skin. Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to thinner skin, which becomes more apparent as they age.
- Sun Exposure:
- Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can accelerate the aging process and contribute to skin thinning. UV radiation damages the collagen fibers in the skin, leading to a loss of elasticity and resilience.
- Medications:
- Long-term use of corticosteroids, whether applied topically or taken orally, can cause thinning of the skin. These medications are often prescribed for conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and asthma. While effective, they can weaken the skin’s structure over time.
- Medical Conditions:
- Certain medical conditions, such as Cushing’s syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, can lead to skin thinning. Cushing’s syndrome is characterized by excessive cortisol production, which can weaken the skin. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects the connective tissues, including the skin.
Symptoms of Thinning Skin
Thinning skin presents with various symptoms that can affect an individual’s quality of life. These symptoms include:
- Fragility:
- Thin skin is more susceptible to cuts, tears, and bruising. Even minor bumps or scrapes can result in significant skin damage.
- Transparency:
- As the skin thins, it may become more translucent, allowing veins and other underlying structures to become more visible.
- Wrinkling and Sagging:
- Reduced collagen and elastin levels lead to increased wrinkling and sagging of the skin. This is particularly noticeable on the face, neck, and hands.
- Dryness:
- Thinning skin often lacks moisture, leading to dryness and an increased risk of developing eczema or other skin irritations.
- Slow Healing:
- Thin skin takes longer to heal from injuries, increasing the risk of infections and complications.
Treatment and Prevention of Thinning Skin
While it is not always possible to completely reverse thinning skin, various treatments and preventive measures can help manage the condition and improve skin health.
- Skincare Routine:
- Establishing a good skincare routine is crucial for maintaining skin health. Using gentle cleansers, moisturizers, and sunscreens can help protect the skin from further damage. Products containing ingredients like hyaluronic acid, retinoids, and peptides can also promote collagen production and improve skin thickness.
- Sun Protection:
- Protecting the skin from UV radiation is essential in preventing further thinning. Wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, avoiding peak sun hours, and wearing protective clothing can help reduce sun damage.
- Healthy Diet:
- A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamins A, C, and E, can support skin health. These vitamins are known for their antioxidant properties, which help protect the skin from damage and promote collagen production.
- Hydration:
- Staying well-hydrated is important for maintaining skin elasticity and preventing dryness. Drinking plenty of water and using hydrating skincare products can keep the skin supple and resilient.
- Medical Treatments:
- For individuals with severe skin thinning, medical treatments may be necessary. These can include prescription-strength retinoids, which stimulate collagen production, and laser therapy, which can improve skin texture and thickness. Dermatologists may also recommend microneedling, a procedure that involves creating tiny punctures in the skin to stimulate collagen production.
- Avoiding Harmful Practices:
- Avoiding practices that can exacerbate skin thinning, such as excessive use of corticosteroids, smoking, and exposure to harsh chemicals, is crucial. If corticosteroids are necessary, they should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize the risk of skin thinning.
Coping with Thinning Skin
Living with thinning skin can be challenging, but there are ways to cope with the condition and maintain a good quality of life.
- Protective Clothing:
- Wearing long sleeves, gloves, and protective padding can help prevent injuries and reduce the risk of skin tears and bruises.
- Gentle Handling:
- Handling the skin gently, using soft towels, and avoiding rough scrubbing can prevent further damage.
- Regular Check-Ups:
- Regular visits to a dermatologist can help monitor the condition of the skin and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
- Emotional Support:
- Dealing with the visible signs of thinning skin can be emotionally challenging. Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can help individuals cope with the psychological impact of the condition.
Conclusion
Thinning skin is a common condition that can result from aging, genetics, medical conditions, and certain medications. While it can present with various symptoms and challenges, understanding the causes and implementing appropriate treatments and preventive measures can help manage the condition effectively. By adopting a comprehensive approach to skincare, sun protection, and a healthy lifestyle, individuals can improve the health and resilience of their skin, enhancing their overall quality of life. Regular consultation with a dermatologist is essential for personalized care and effective management of thinning skin.