Understanding Photosensitivity: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
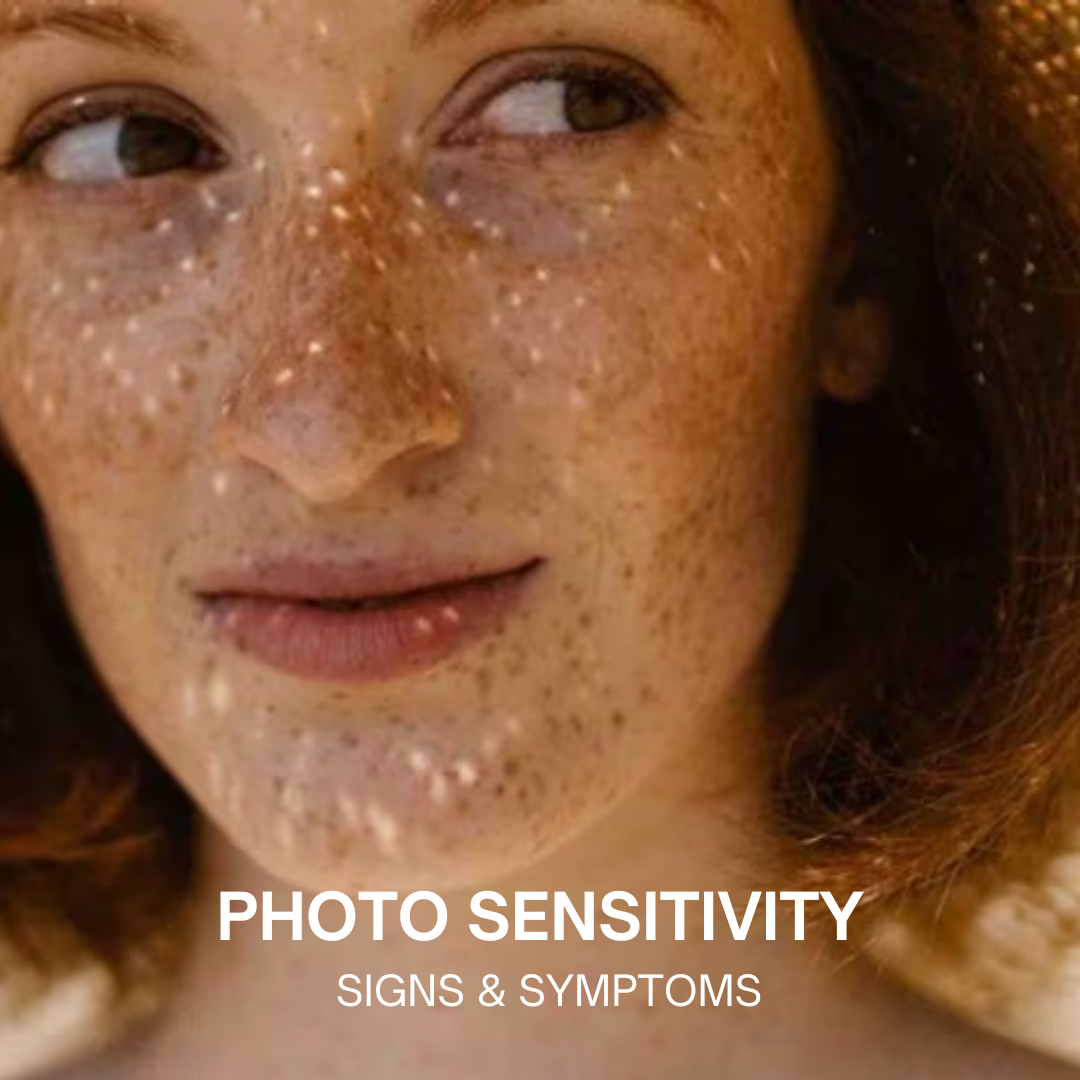
Photosensitivity, also known as sun sensitivity, is a condition where an individual’s skin reacts abnormally to sunlight or artificial ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This heightened sensitivity can lead to a variety of skin reactions, from mild redness to severe blistering and rashes. Understanding photosensitivity is crucial for those affected by it, as well as for healthcare providers aiming to manage and treat this condition effectively.
Causes of Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity can be triggered by various factors, including medications, medical conditions, and genetic predispositions. Below are some of the primary causes:
- Medications:
- Antibiotics: Drugs like tetracycline and doxycycline are known to cause photosensitivity.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications such as ibuprofen can increase sensitivity to sunlight.
- Diuretics: Commonly prescribed for hypertension, these can also lead to sun sensitivity.
- Antifungals and Antidepressants: Certain drugs in these categories can make the skin more prone to UV damage.
- Medical Conditions:
- Lupus: An autoimmune disease that often causes a characteristic rash in response to sun exposure.
- Porphyria: A group of disorders caused by abnormalities in the chemical steps leading to heme production, which can cause severe photosensitivity.
- Polymorphous Light Eruption (PMLE): A common sun allergy resulting in a rash upon sun exposure.
- Genetic Factors:
- Certain genetic conditions, such as xeroderma pigmentosum, lead to extreme sensitivity to UV light due to defects in DNA repair mechanisms.
Symptoms of Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity manifests through various symptoms, which can range from mild to severe. These symptoms typically appear within minutes to hours after sun exposure and can last for days or even longer. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and Swelling:
- The affected skin area becomes red and swollen, similar to sunburn but often more severe and painful.
- Rashes:
- A variety of rashes can occur, including red patches, blisters, or hives. These rashes can be itchy and uncomfortable.
- Blisters and Peeling:
- Severe cases of photosensitivity can lead to blistering and peeling of the skin, similar to severe sunburn.
- Hyperpigmentation:
- Some individuals may experience darkening of the skin in affected areas, which can persist even after the initial symptoms have subsided.
- Other Systemic Symptoms:
- In cases associated with underlying conditions like lupus, individuals may experience joint pain, fever, and fatigue.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing photosensitivity involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and sometimes specialized tests. Healthcare providers will often ask about recent sun exposure, medication use, and any underlying medical conditions. Diagnostic tools include:
- Phototesting:
- This involves exposing small areas of skin to UV light and observing the reaction. It helps determine the specific wavelength of light causing the sensitivity.
- Blood Tests:
- These can identify underlying conditions like lupus or porphyria that might be contributing to photosensitivity.
- Skin Biopsy:
- In some cases, a small sample of skin is taken to examine under a microscope, which can help diagnose certain conditions causing photosensitivity.
Management and Treatment
Managing photosensitivity involves a multifaceted approach, including prevention strategies, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatments.
- Prevention:
- Sun Protection: Wearing protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses can help shield the skin from UV rays. Using broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF is essential.
- Avoiding Peak Sun Hours: Staying indoors during peak sunlight hours (10 AM to 4 PM) can reduce exposure to harmful UV radiation.
- UV-Protective Films: Applying UV-protective films to windows can help reduce indoor exposure to UV rays.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Adjustments: Some studies suggest that certain foods rich in antioxidants, like fruits and vegetables, can help reduce skin sensitivity to sunlight.
- Medication Review: If medications are causing photosensitivity, healthcare providers may adjust the dosage or prescribe alternative drugs.
- Medical Treatments:
- Topical Steroids: These can help reduce inflammation and soothe the skin in cases of mild to moderate photosensitivity.
- Oral Medications: In severe cases, oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive drugs may be prescribed to manage the condition.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to UV light under medical supervision can sometimes help build tolerance in individuals with certain types of photosensitivity.
- Alternative Therapies:
- Supplements: Some supplements, like beta-carotene and nicotinamide, have been found to provide some protection against sunburn and photosensitivity.
- Natural Remedies: Aloe vera and chamomile can provide soothing relief for sunburned or irritated skin, although their effectiveness in treating photosensitivity specifically is not well-established.
Living with Photosensitivity
Living with photosensitivity requires ongoing vigilance and proactive management. Here are some tips for coping with the condition:
- Education and Awareness:
- Understanding your specific triggers and learning how to avoid them is crucial. Stay informed about new treatments and management strategies.
- Support Networks:
- Connecting with support groups or online communities can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who share similar experiences.
- Regular Medical Check-ups:
- Regular visits to a dermatologist or healthcare provider can help monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Documentation:
- Keeping a diary of sun exposure, symptoms, and reactions to treatments can help you and your healthcare provider better understand and manage the condition.
Conclusion
Photosensitivity is a challenging condition that requires careful management and a proactive approach to prevention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, individuals can take control of their condition and reduce its impact on their daily lives. With the right strategies in place, those affected by photosensitivity can continue to enjoy a fulfilling and active lifestyle while minimizing the risks associated with sun exposure.