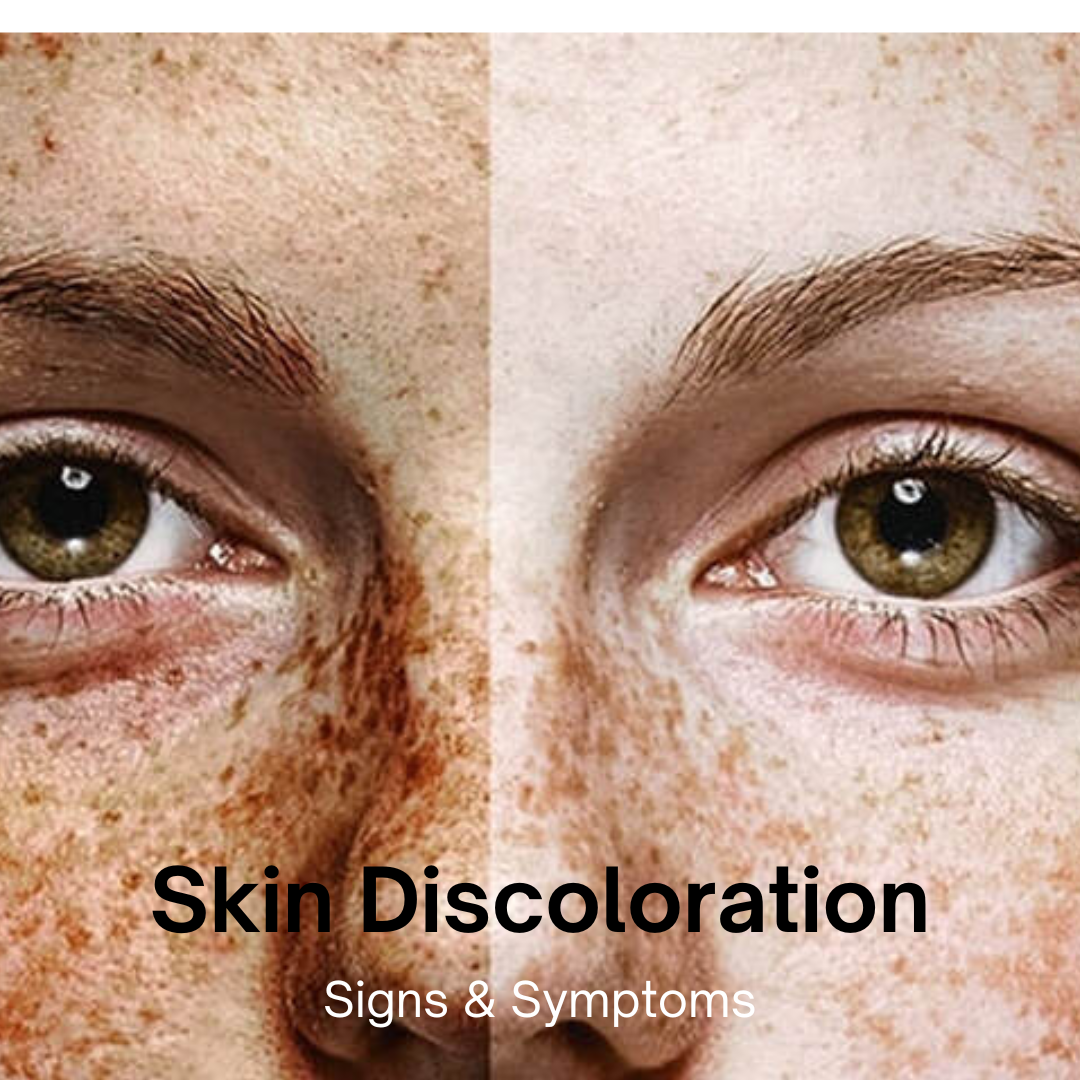
Understanding Skin Discoloration: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
Skin discoloration refers to any changes in the natural tone or color of the skin. This can manifest as dark spots, light patches, redness, or other variations from the normal skin color. It is a common dermatological concern that can affect individuals of all ages and skin types. Understanding the causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies for skin discoloration is crucial for maintaining healthy, even-toned skin.
Causes of Skin Discoloration
- Hyperpigmentation
- Melasma: Often caused by hormonal changes, melasma presents as dark patches, typically on the face. It is common during pregnancy or with the use of birth control pills.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): This occurs following skin injury or inflammation, such as acne, eczema, or cuts. The affected area becomes darker than the surrounding skin as it heals.
- Sun Exposure: Excessive sun exposure increases melanin production, leading to sunspots or age spots, particularly in sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, and shoulders.
- Hypopigmentation
- Vitiligo: A condition where the immune system attacks melanocytes (pigment-producing cells), leading to white patches on the skin.
- Albinism: A genetic condition characterized by a lack of melanin production, resulting in very light skin, hair, and eyes.
- Pityriasis Alba: Common in children, this condition causes pale patches on the face and upper body, often associated with eczema.
- Red and Inflamed Skin
- Rosacea: A chronic condition causing redness and visible blood vessels, primarily on the face.
- Erythema: Generalized redness often due to inflammation, infection, or irritation.
- Allergic Reactions: Exposure to allergens can cause red, itchy, and swollen skin.
- Other Causes
- Bruising: Blood vessels under the skin break, causing a purple, blue, or greenish discoloration as the blood is absorbed.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause skin discoloration as a side effect. For example, antimalarial drugs and some antibiotics can lead to darkening of the skin.
Treatment Options for Skin Discoloration
- Topical Treatments
- Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that reduces hyperpigmentation. It should be used under medical supervision to avoid potential side effects.
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, retinoids promote cell turnover and can help in treating hyperpigmentation and improving overall skin texture.
- Vitamin C: Known for its antioxidant properties, vitamin C can brighten the skin and reduce the appearance of dark spots.
- Corticosteroids: Used for conditions like eczema and psoriasis, corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and discoloration.
- Chemical Peels
- Chemical peels involve applying a solution to the skin that causes it to exfoliate and eventually peel off. This can improve the appearance of hyperpigmented areas and even out skin tone.
- Laser Therapy
- Laser treatments target the pigment in the skin, breaking down melanin and promoting an even skin tone. Different types of lasers are used depending on the specific discoloration issue.
- Microdermabrasion and Dermabrasion
- These procedures mechanically exfoliate the top layers of the skin, promoting new skin growth and reducing discoloration.
- Phototherapy
- Light therapy, particularly for conditions like vitiligo, can help in repigmenting the skin.
Prevention of Skin Discoloration
- Sun Protection
- Using broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 daily can prevent sun-induced hyperpigmentation and protect against UV damage.
- Wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses can also minimize sun exposure.
- Skin Care Routine
- Regular cleansing, moisturizing, and exfoliating can help maintain healthy skin and prevent issues like acne and inflammation that can lead to discoloration.
- Using products suited to your skin type and avoiding harsh chemicals can reduce the risk of irritation and discoloration.
- Diet and Hydration
- A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants supports skin health. Staying hydrated ensures the skin remains supple and less prone to irritation and discoloration.
- Avoiding Triggers
- Identifying and avoiding known allergens or irritants can prevent allergic reactions and associated skin discoloration.
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and sufficient sleep can also help maintain skin health.
- Medical Advice
- Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can help detect and manage skin conditions early, preventing severe discoloration.
Conclusion
Skin discoloration can be a source of discomfort and self-consciousness for many individuals. By understanding its causes, exploring effective treatment options, and adopting preventive measures, it is possible to achieve and maintain an even, healthy skin tone. Consultation with a dermatologist is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment, ensuring that the chosen methods are safe and effective for your specific skin type and condition.